Why Mammography Machines Are Essential in Early Breast Cancer Detection
Understand how digital breast imaging systems detect cancer early—and why clinics worldwide trust this life-saving technology.
In the global fight against breast cancer—one of the most common cancers affecting women today—early detection remains the strongest weapon. Among all diagnostic tools available, digital mammography systems stand out as the gold standard for identifying early-stage abnormalities, often years before symptoms appear.
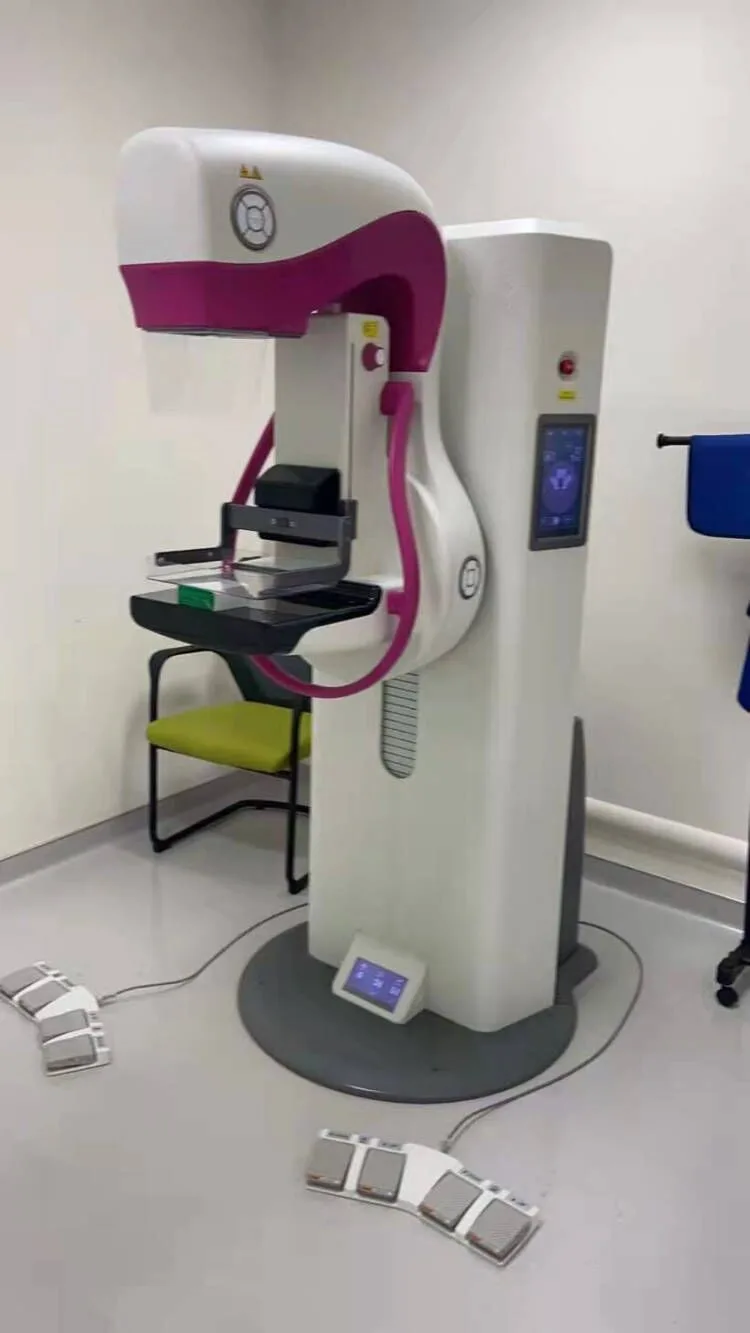
These specialized X-ray devices, sometimes referred to as mammogram machines or breast imaging systems, are not ordinary radiography tools. They are engineered with precision to capture high-resolution images of soft breast tissue while minimizing radiation exposure.
But what makes a mammography machine different from regular X-ray equipment? And why is it so crucial in preventive healthcare—especially for women over 40?
Let’s explore how this life-saving technology works, its evolution, and why clinics and hospitals worldwide rely on it for effective screening programs.
🌟 The Science Behind Breast Imaging: How Mammography Machines Work
Unlike general X-rays designed for bones or lungs, mammography systems use low-energy X-rays generated by molybdenum (Mo) or rhodium (Rh) targets. This unique setup produces a specific spectrum of radiation ideal for visualizing delicate breast structures.
- Optimized wavelength: Enhances contrast between fatty and glandular tissues
- Reduced radiation dose: Typically less than 0.4 mSv per scan—comparable to a few days of natural background radiation
- High spatial resolution: Capable of resolving microcalcifications as small as 0.1 mm, an early sign of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)
To achieve clear results, the breast is gently compressed between a plastic paddle and an imaging detector. While some patients report mild discomfort, this step ensures:
- Thinner tissue layers → clearer images
- Less X-ray scatter → lower dose required
- Reduced motion blur
Modern units feature automatic exposure control, adjusting settings based on breast density and thickness for consistent image quality.
📸 Standard Views in Clinical Practice
During a routine screening, two primary projections are captured per breast:
- Craniocaudal (CC) – Top-down view
- Mediolateral Oblique (MLO) – Diagonal side view
These angles together provide comprehensive coverage of the breast tissue, including areas near the chest wall and axilla (armpit), where tumors may develop silently.
Each exposure takes only seconds, and the entire procedure typically lasts under 20 minutes. Patients are advised to avoid deodorants, powders, or lotions on the day of the exam to prevent artifacts on the image.
🎯 Why Mammography Saves Lives: Proven Impact on Mortality
Numerous large-scale studies—including data from the WHO and American Cancer Society—show that organized mammography screening programs reduce breast cancer mortality by up to 40% in women aged 50–69.
Even more encouraging: when cancer is detected at stage 0 or stage I, the 5-year survival rate exceeds 99%.
🚀 Advancing Precision: 3D Tomosynthesis (Digital Breast Tomosynthesis – DBT)
Traditional 2D mammography has limitations—especially in dense breast tissue, where overlapping structures can mask small lesions or mimic cancer (false positives).
Enter 3D digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT)—a cutting-edge upgrade now integrated into advanced mammography systems.
How it works:
- The X-ray tube moves in an arc across the breast
- Captures multiple low-dose images from different angles
- A computer reconstructs them into thin slices (1 mm thick)—like flipping through the pages of a book
| Feature | 2D Mammography | 3D Tomosynthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Cancer Detection Rate | Baseline | ↑ Up to 40% higher |
| False Positive Recall | Higher | ↓ Reduced by ~15% |
| Accuracy in Dense Breasts | Moderate | Significantly Improved |
🏥 Who Should Use Mammography Equipment?
International health organizations agree on the importance of regular screening:
| Organization | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| USPSTF | Biennial screening for women 50–74 |
| ACR | Annual screening starting at age 40 |
| WHO | Organized programs for women 50–69 |
For medical facilities, investing in FDA-cleared, CE-marked mammography machines ensures compliance with international safety and image quality standards— critical for clinics serving expatriates, international patients, or telehealth referrals.
💡 Conclusion: Early Detection Starts with the Right Technology
Breast cancer doesn’t wait—and neither should you. With modern mammography machines, especially those featuring 3D tomosynthesis, early detection is more accurate, safer, and more accessible than ever.
🔑 Final Takeaway:
A few minutes of compression could save decades of life. Prioritize screening. Invest in precision. Protect health.
If you operate a clinic, hospital, or women’s health center abroad, offering certified mammography services not only meets global standards— it builds trust, improves outcomes, and enhances your reputation in competitive healthcare markets.